What is dysmenorrhea?
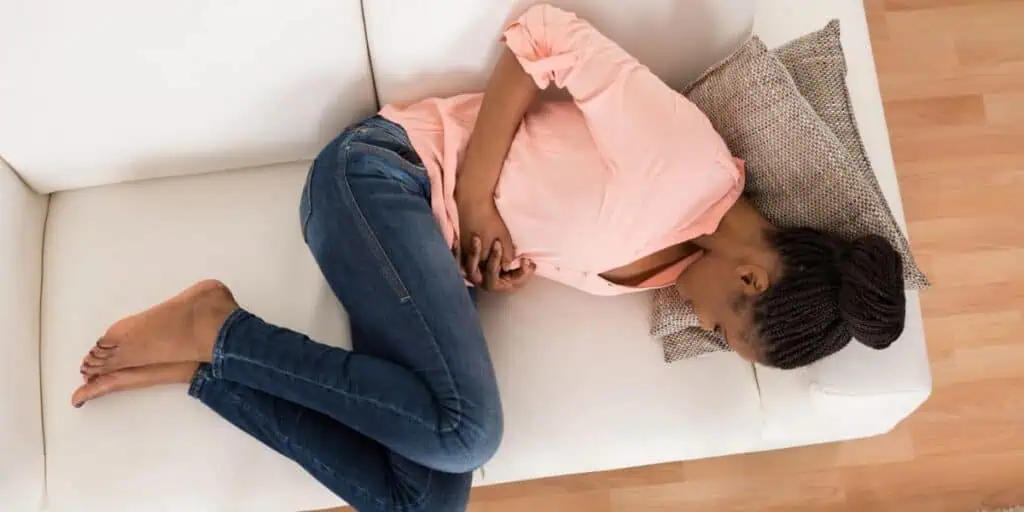
The medical term for painful menstrual periods or menstrual cramps is called dysmenorrhea, and it’s one of the most common menstrual disorders. It affects over half of menstruating women for at least one day throughout a menstrual cycle.
It affects a large percentage of women of reproductive age, varying from 20 to 90%. Being the most common menstrual disorder, it typically starts within a year of the first menstrual period. Often, the pain improves with age or after giving birth.
Dysmenorrhea occurs less often in those who exercise regularly and those who have children early in life.
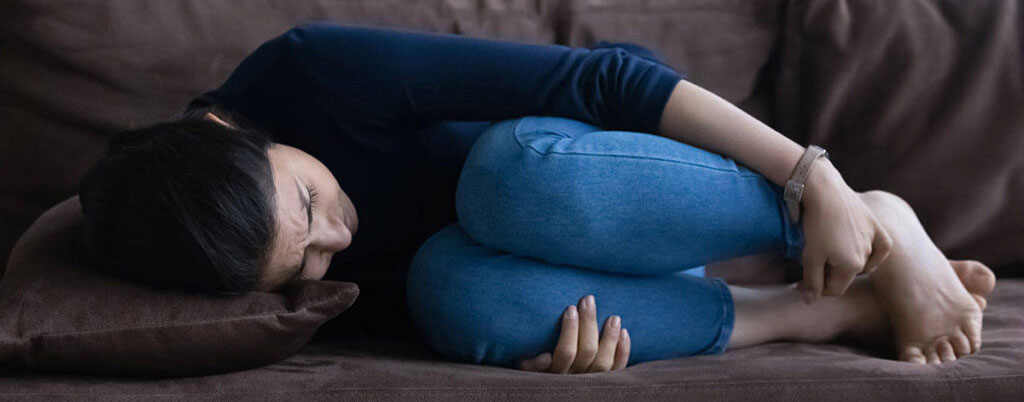

What are the symptoms of dysmenorrhea?
Menstrual pain symptoms will typically last less than three days, but in some, it is longer. Usually, the pain occurs in the pelvis or lower abdomen and can radiate to your lower back and thighs. Other symptoms may include diarrhea or nausea.
Dysmenorrhea is more common among those with heavy menstrual bleeding, irregular menstrual periods, those whose periods started before twelve years of age, or those who have low body weight, possibly anemic.
What are the two types of dysmenorrhea?
Dysmenorrhea can be classified into two distinct types:
Primary dysmenorrhea
This is what we usually think of as menstrual cramps. The cramping usually starts right before your menstrual period and subsides as you shed the uterine lining. Primary dysmenorrhea typically starts when a young woman is just beginning to menstruate and often becomes less painful as she gets older. For young women, period pain usually occurs without an underlying problem.
Secondary dysmenorrhea
Secondary dysmenorrhea is caused by an underlying reproductive health issue. it is characterized by more severe and longer-lasting pain caused by a problem in the reproductive system. It might start a few days before your menstrual period or continue after it ends.
What causes secondary dysmenorrhea?
Several medical conditions can cause painful periods, including:
- Uterine Fibroids and Cysts. These are growths on the walls of the uterus that can be surgically removed. Fibroids and cysts exert pressure on the uterus and surrounding tissues, increasing menstrual cramps and discomfort.
- Endometriosis. The endometrium is better known as the inner lining of the uterus. When the endometrial cells also grow outside of the uterus, such as on the fallopian tubes, ovaries, or bladder, this is called endometriosis. The endometrial tissue bleeds in response to hormones, which can form scar tissue called adhesions if these cells are outside the uterus. Adhesions disrupt your pelvic organs and cause pain.
- Adenomyosis In this condition, the endometrium starts to grow into the muscular tissue of the uterus, causing inflammation and painful, heavy periods.
- Ovarian cysts. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside an ovary. They can exacerbate menstrual cramps and cause heavy bleeding with periods.
- Cervical stenosis In some women, the opening of the cervix is small enough to impede menstrual flow, causing a painful increase of pressure within the uterus.
Other causes of secondary dysmenorrhea include pelvic inflammatory disease, intrauterine device (IUD) complications, and pelvic adhesion. Your doctor will likely perform a minimally invasive laparoscopy to confirm a diagnosis.
What are the treatments for dysmenorrhea?
If you’re having painful periods, please make an appointment with us. Many women take their painful periods in stride, believing that cramps are just part of the process. If you’re suffering from severe pain, and it’s interrupting your day, it is not considered standard.
We will review your medical history and perform a pelvic exam to evaluate your condition. Conditions should be ruled out, such as ectopic pregnancy, pelvic inflammatory disease, interstitial cystitis, and chronic pelvic pain.
Conservative treatment options include:
- Pain relievers. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (or NSAIDs), such as over-the-counter ibuprofen or naproxen, target prostaglandins, which cause primary dysmenorrhea.
- Hormonal birth control. Oral contraceptives, patches, rings, hormonal birth control pills, and the IUD with progestogen have all been used to successfully treat painful periods, especially those caused by endometriosis. These are often prescribed by a healthcare provider because the hormones thin out the lining of the uterus, which lessens the cramping and the blood flow. These treatments help regulate your body’s hormones and ease some of the more unpleasant effects of menstruation.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists. This is another type of hormone therapy that helps treat endometriosis, but they’re not typically given as a long-term solution. They can cause side effects like hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and bone loss and are usually only recommended in extreme cases.
- Alternative treatments. Home treatment may include using a heating pad or warm bath. Some women have found that taking a vitamin B1 or magnesium supplement can ease painful periods. Others report success with acupuncture.
Surgical treatments for dysmenorrhea include:
- Uterine artery embolization. Generally performed on an outpatient basis, this procedure blocks uterine blood vessels with tiny particles to stop the growth of uterine fibroids.
- Surgical removal of uterine fibroids. This is performed through a small incision either through the vagina or abdomen, depending on the location of the fibroid.
- Surgical treatment of endometriosis. This usually relieves pain in the short term, but it does not prevent the endometriosis from returning. Fortunately, the regrowth of tissue can be delayed with hormonal treatment.
- Complete removal of the uterus is typically performed only as a last resort.
Make an appointment with Dr. Aliabadi
Don’t let painful periods define your life. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Aliabadi and receive personalized expert care.
As one of the nation’s leading OB/GYNs, Beverly Hills’ Dr. Thaïs Aliabadi offers the very best in women’s health and well-being. With her warm, professional team, Dr. Aliabadi supports women through all phases of life. She fosters a special one-on-one relationship between patient and doctor.
Dr. Aliabadi specializes in up-to-date, minimally invasive surgical techniques, promising her patients shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and the least interruption to their daily lives.
We also invite you to establish care with Dr. Aliabadi. Please make an appointment online or call us at (844) 863-6700 for general inquiries.
Sources
Aromatherapy for Managing Pain in Primary Dysmenorrhea: A Systematic Review of Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials – PMC
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6262530/
Uterine fibroids – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/uterine-fibroids/symptoms-causes/syc-20354288