What is Abnormal Uterine Bleeding?
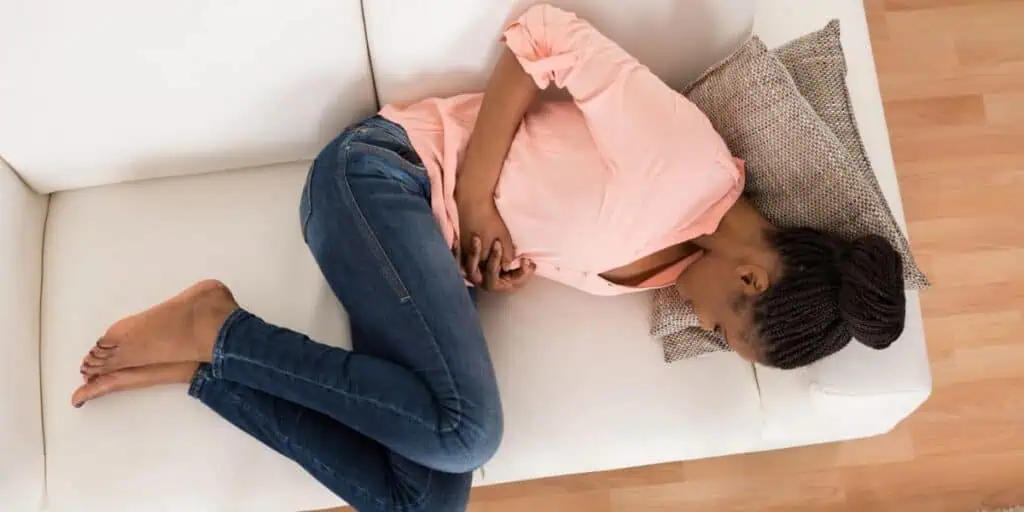
A normal menstrual cycle occurs every 28 days, and the period of bleeding lasts anywhere from 3 – 7 days. In women’s health, Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is bleeding that occurs outside of this pattern and sometimes indicates that there is a problem with your cervix or uterus.

AUB is a condition that has many causes. Pregnancy is usually a common cause. Polyps in the uterus or uterine fibroids can also cause bleeding as well as menstrual disorders. Rarely, a thyroid problem, infection of the cervix, or maybe cancer of the uterus can cause abnormal uterine bleeding.
But in most women, abnormal uterine bleeding is caused by an imbalance of their hormones. When hormones are the problem, health care providers call the problem dysfunctional uterine bleeding or DUB. Abnormal bleeding caused by hormone imbalance is more common in teenagers or perimenopausal women.
With postmenopausal women, AUB includes vaginal bleeding 12 months or more after your menstrual cycles have stopped or unpredictable bleeding in postmenopausal women who have been receiving hormone therapy for 12 months or more.
For instance, girls ages 9-15 might experience some abnormal bleeding while their menstrual cycles are just getting started. Additionally, as women approach the age of menopause their cycles may get longer or they may skip a period once in a while. These are both examples of times when women’s monthly cycles are adjusting to their fluctuating levels of hormones.
Abnormal bleeding can be described as:
- Spotting or bleeding between periods
- Heavier menstrual bleeding
- Bleeding for a longer period of time than normal
- Bleeding after sex
- Bleeding after menopause
- Lack of menstrual bleeding for 3-6 months, also known as amenorrhea
While abnormal bleeding may indicate that something is wrong, some irregular bleeding can be normal at certain stages of life.
Causes of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Sometimes, abnormal bleeding can signal a more serious problem. Some common causes include:
- Infections (cervical or uterine)
- Issues with a birth control device (IUD or pills)
- Blood clotting problems
- Fibroids
- Polyps
- Pregnancy
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Adenomyosis (a disorder of the endometrial tissue)
- Endometrial hyperplasia
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome
- Cervical, uterine, or vaginal cancer
- Endometrial polyps
If you’re concerned about abnormal uterine bleeding, please make an appointment with us so we can review your medical history and perform a full physical examination and workup. If you can, keep a log of the dates that you begin and stop bleeding, and record whether the bleeding was light, medium, or heavy, and as well as any other symptoms you may have.
We may want to check your blood count to make sure your blood count isn’t too low from the blood loss. This could lead to iron deficiency and anemia as well.
Testing and Diagnosis of Abnormal Bleeding
Abnormal bleeding can have a wide range of possible causes. At your appointment, we’ll perform a pelvic exam and ultrasound. We may ask that you take a blood test and/or a pregnancy test.
Some other tests can help with diagnosis as well. Depending on the results of your exam and blood test, we may want to get a better idea of what’s going on in your uterus by using:
- MRI
- Sonohysterography – A procedure in which an ultrasound is performed after the uterus is filled with fluid.
- Hysteroscopy – A long, thin device with a light and camera at the end is inserted through the cervix to view the inside of the uterine cavity.
- Endometrial biopsy – A sample of endometrial tissue is taken from the uterine lining and examined under a microscope.
Treatment for Abnormal Bleeding
Your particular course of treatment will depend upon your diagnosis, age, and family planning wishes.
Women who have abnormal or heavy periods are sometimes prescribed, oral contraceptives (birth control pills) or other hormone therapy, such as gonadotropin-releasing hormone (injections, rings, creams, or an intrauterine device (IUD)). These hormones can lighten menstrual flow. They also help make your menstrual periods more regular. Your doctor can discuss your options and possible side effects with you. Some women have to try a few different types of hormonal treatment before they find the one that works for them.
Other drugs used to treat abnormal bleeding include antibiotics (for infections) and NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) like ibuprofen, which can control heavy bleeding and ease cramping.
If medication does not reduce your abnormal bleeding, a surgical procedure may be needed. Uterine polyps or fibroids are often removed surgically. Under certain circumstances, endometrial ablation or complete hysterectomy may be recommended. Endometrial ablation is a surgical procedure that destroys the lining of the uterus. Unlike a hysterectomy, it does not remove the uterus.
Endometrial ablation may stop all menstrual bleeding in some cases. These surgeries will permanently reduce bleeding or stop the bleeding entirely and should only be performed when a woman is sure that she no longer wants to get pregnant.
Make an appointment with Dr. Aliabadi
Don’t let painful periods define your life. Schedule a consultation with Dr. Aliabadi and receive personalized expert care.
As one of the nation’s leading OB/GYNs, Beverly Hills’ Dr. Thaïs Aliabadi offers the very best in women’s health and well-being. With her warm, professional team, Dr. Aliabadi supports women through all phases of life. She fosters a special one-on-one relationship between patients and doctors.
Dr. Aliabadi specializes in up-to-date, minimally invasive surgical techniques, promising her patients shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and the least interruption to their daily lives.
We also invite you to establish care with Dr. Aliabadi. Please make an appointment online or call us at (844) 863-6700 for general inquiries.